Whether one builds a website, app, SaaS product, or any digital product, UI and UX are the most crucial elements of the process that are required to begin the process for the same.
User interface (UI) and User experience (UX) are the two most often confused and conflated terms in the process of product development.
Moreover, these terms are usually used in general and viewed from a superficial space and are often misused and misunderstood by people, in the World of digital product design and development. This article aims to clarify the concept and dive deeper into understanding UI/UX design and explore the nuances between them.
So, let’s begin! 🚀
What is UI Design?
The UI is the graphical layout of an application or a digital product which represents how the application or the digital product would appear in the terms of look and feel of the same.
It also includes transitions, micro-interactions, and animations that consist of all the various elements that the user interacts with that is, colors, typography, buttons, images, sliders, text fields, and so on and so forth.
Out of the many types of User interfaces, these are 3 most used UI interfaces, namely:
Command line interface (CLI)
Graphic user interface (GUI), and
and voice-enabled interface
Maintaining the UI Interface is the key responsibility of the UI Designer. The look and feel of the product design and branding are one of the prime focuses of the UI Designer.
From choosing the color schemes, button shapes, line widths and font styles to creating the look and feel of an application’s user interface (UI), a UI designer knows, and does it all!
UI designers are the people who design the look and feel of an application or product. Their tasks may include choosing between different color schemes or button shapes. UI designers are also responsible for deciding whether every single visual element feels united, both aesthetically, and in purpose.
UI designers are also responsible for deciding on a unified single visual element both in terms of aesthetics, and purpose, helping to set the branding on point.
Now, the prime question, that might arise in one’s mind is, what are the essential properties of a well-designed UI?
Essential properties of well-designed UI
No matter what UI you design, it should comply with the following criteria:
Clarity. UI elements are designed to be easily understood and simplified for all users. Most UI elements will have an icon or a text description to help new users on the website help understand what is being displayed.
Consistency. Keeping the interface (including features) of your app consistent across the entire product allows users to more easily recognize those features and help in establishing a unified branding.
Familiarity. Your UI is designed to enable users to reuse existing knowledge and skills when they interact with your product, on a consistent and regular basis.
Forgiveness. Good interfaces should provide an experience in which users can easily recover from their errors, so that the users can use the features to the full possible utilization, without the fear of making mistakes.
Efficiency. A Good User Interface provides minimal input for people to achieve their desired results. It also allows experienced users to take shortcuts in order to complete tasks even faster and be more efficient in deriving results.
Interface design methods
The primary interface design techniques are wireframing, prototype, and simulation.
Wireframing. Based on the brainstorming and ideation sessions with the customer, UI designers create a low-fidelity wireframe.
Prototype. Wireframes are put together inside of the process flow to connect them with the business story.
Simulation. Simulation is a part of validating the design decisions by testing a prototype with people that represent the target audience (the group of people/audience who will be using the product.)It’s an essential part of the usability test sessions.
Towards the end, the product team provides the prototype & the pre-defined task to the targeted audiences and stakeholders to be able to see how they are navigating through.
Notes are usually taken out of the usability testing.
What is User Experience & UX Design?
The term “user experience” was coined in 1995 by Don Norman, who was also known as the father of cognitive science.
He wanted to call it “human factors engineering” but changed his mind as soon as he realized that the term was too long and unwieldy.
User experience (UX) design, on the contrary, is a multi-disciplinary field that combines aspects of all namely, psychology, graphic design, and human-computer interaction to improve the usability of the product.

UX design is the process of enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty by making products easier to use.
If a product has a good user-experience, customers are more satisfied with it, eventually getting more pleasure from interacting with it.
User persona
UX design’s initial step is to create the User persona.
UX Designers are expected to understand their target audience and identify exactly what they need from the product. They achieve this by creating User Personas which in turn help users see their goals, desires, and limitations better.
These learnings from the past allow them to create design solutions that work best for the users, who may come from all sorts of varied backgrounds.
User journey concept
The emotions that a user has while using a product can have a bigger effect on how they feel about the product. That’s why the user experience design is all about mapping the ideal journey for the customers to follow while interacting with the product. Describing good and bad user journeys will help one make any necessary changes to one’s product.
UX works to improve a user’s experience in order to help them solve their specific problem. The UI also helps in this process.
Design is the magical ingredient that helps in improving the UX experience.
What makes good UX design?
According to Aaron Walter’s idea of “pyramid of needs”, a user has an individual pyramid with levels that need to be fulfilled in order.
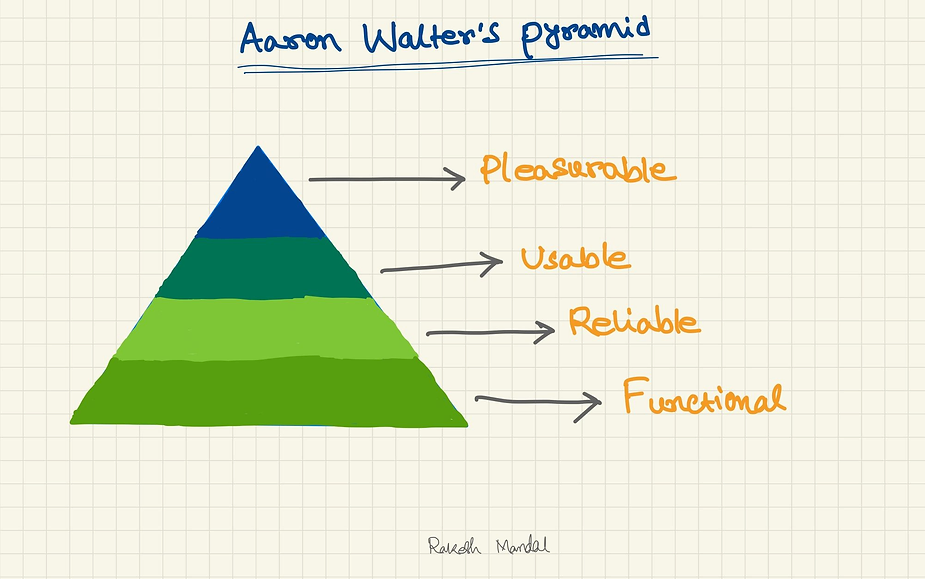
To create a good product, one needs to start with a good foundation.
The most important thing is functionality, followed by reliability (securing the data).
Furthermore, usability and pleasure are both desirable parts of the experience. When all the needs are satisfied gradually, the user is happy and one’s goal is achieved.
How UI & UX are Related to Each Other
Simply put, the UI and UX indicate that they are related to the design disciplines. However, they are very different in nature.
The focus while designing of the UI is largely on aesthetics and mostly on the look and feel of the same. Without a good UX, even the most visually pleasing UI will produce a frustrating experience for the users.
The role of UX designers
Primitively, designing was not a key factor for many companies, but that has gradually over the decades, changed. Nowadays, companies have realized that a good design is a competitive advantage in comparison to the competitors in the market and the organizations are willing to invest a significant amount of resources in it.
Simply put, a UX design is a human-centered way of designing products.
UX designers analyze people’s needs and research the user base to ensure that the company creates products that satisfy those needs.
For the design process, UX designers can be involved in many facets such as research, ideation, prototyping, usability testing.
The role of a UX designer usually includes:
Understanding users. UX design starts with understanding the audience and designing the products that suit their need. Empathy is a primary key skill for UX designers, as it helps them analyze the user needs and emotions, of the target audience.
Creating a design strategy. A design strategy is important because it helps to spread awareness, create a ton of loyal followers, and increase revenue.
Analyzing the design of interactions. UX designers think about how people use their products in order to find out what works and what doesn’t. They notice how the target audience, that is the users, interact with the interface, along with the user’s personal preferences and habits. This information is used to guide the design process so that a better solution can be found.
Creating wireframes and prototypes. UX designers often work with UX design software to create wireframes or prototypes, which they then present to the designing team to convey the idea and inspiration behind it.
UX designer is involved in the execution of the entire product, and in the discussions with the team members who are making sure the design of the product is shaping up as planned.
The role of UI designers
The role of the UI Designer is focused on the visual representation of information. For this, it’s important to have a good graphic design and visual design skills.
Having the designing skills of creating brand elements is also important as they help create an interface that has a professional look & feel. In usual practice, the UI designers take the same UX designs and wireframes and then dress it up to make it more aesthetically pleasing. The designer starts with a skeleton of designs created by the UX designer (skeleton) and then brings out the best features.
Being a good designer means a few things, such as:
Attention to detail. Good designers understand that “the devil is in the details” and will always work on perfecting it! This includes small details even to their own solutions.
Good problem-solving skills. Designers need to be aware that they solve a problem with every design they make! Designers should be ready to spend their time in finding the best solutions.
As a UI designer, there are a few things that are relevant in the process:
Competitive analysis. To be able to analyze and conduct competitive analysis of product and visual designs.
Responsive design. Ensuring that the UI design works great across all screen sizes and resolutions.
Communication. UI designers usually work closely with UX designers as well as the engineering team. They need quite a lot of communication and coordination skills to be able to understand how feasibly their designs can be utilized by the engineering team.
Conclusion
In conclusion, would like to wrap up by saying that UX design is rooted in cognitive behavior & human psychology, along with the final user experience. UI design focuses more on how things look and whether a product is aesthetically pleasing, or not.
It’s important to identify the type of design that your brand is interested in and focus on honing the skills that are required to execute it. For those new to designing World, I recommend you try your hands in both areas.
Practical experience in both fields will help you figure out which area is best suited for you while making you a better designer!
